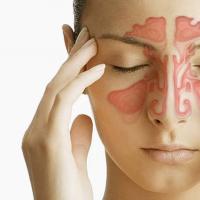
Colpitis - what is it: symptoms and treatment
From vaginal infections, the vagina is protected by the acidic environment of the mucous membrane. However, under the influence of various factors, the sensitive environment responsible for protecting the female genital organs can get out of balance, allowing pathogenic microorganisms to multiply. One of the consequences of such a process is colpitis.
Colpitis disease
This disease is more common in women of childbearing age, but can occur in older women or even young girls. Colpitis - what is it? The disease belongs to the category of infectious and inflammatory, while the vaginal mucosa is affected by pathogenic microorganisms (Hemophilus influenzae, streptococcus, staphylococcus, Escherichia coli, fungi of the genus Candida, etc.).
The disease of colpitis in the international classification (ICD) has the code N70-N77, its second name is vaginitis. A disease develops in the vagina as a result of infection of the internal environment of the genital organs, violations of metabolic or endocrine functions, injuries. The main signs of colpitis are profuse discharge of a cloudy color, pain in the lower peritoneum and in the vagina, itching. The inflammatory process can proceed in an acute or chronic form.
spicy
Inflammation of the genital organs with such a disease occurs suddenly. Signs that characterize acute colpitis are:
- burning sensation in the vagina and labia;
- pain of internal localization;
- admixture of ichor in secretions;
- feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen.
When examining the vagina, the mucous membrane of the genital organs of a woman has a swollen, reddened appearance, with the slightest impact on it (careless introduction of gynecological mirrors) begins to bleed. The consequence of the inflammatory process may be the further spread of infection to the external genitalia and cervix. The course and symptoms of colpitis depend on the age, the state of the woman's immunity, the type of pathogen that caused the disease, and other individual factors.
Chronic
What is chronic colpitis? When a woman ignores the symptoms during the acute course of the disease, the infection goes into a latent state, as a result of which the form of the pathology is transformed into a chronic one. At the same time, the disease practically does not show itself, with the exception of periods of exacerbation. Chronic colpitis is characterized by a gradual spread of infection to other organs of the female reproductive system - fallopian tubes, ovaries, uterus.
In pregnant women
Inflammation of the vaginal mucosa in women in position leads to serious inconvenience, while the pathological process can worsen and pose a danger to the fetus. Colpitis during pregnancy threatens to infect the baby or amniotic fluid, as a result of which various complications can develop. In pregnant women, vaginitis can be bacterial or infectious, both of which are associated with a malfunction of the immune system or hormonal imbalance.
Colpitis - causes
The acidic vaginal flora serves as a reliable barrier that protects the genitals from the penetration of pathogenic microbes that cause colpitis. Doderlein sticks (the basis of a healthy flora) maintain a normal vaginal environment only if the ovaries work normally, which produce hormones responsible for updating the cells of the genital mucosa.
What are the causes of colpitis in women? Any disease, especially endocrine, disrupts the body's natural physiological processes, including the balance of hormones. As a result, the vaginal microflora undergoes a change: its protective properties deteriorate, fungal and other pathogenic organisms begin to multiply uncontrollably, and the woman develops symptoms of vaginitis. As a rule, the causative agents of the disease are gardnerella, Trichomonas, Escherichia coli, staphylococci, streptococci.
atrophic
The disease is typical for the postmenopausal period, in addition, it can develop in women with artificially induced menopause. Due to a decrease in the level of estrogen, a symptom complex occurs, which is manifested by itching, dryness, discomfort in the vaginal area, pain during intercourse, bloody discharge after sexual intercourse. Atrophic colpitis (aka senile), as a rule, develops due to estrogen deficiency, which leads to a decrease in the secretion of the vaginal glands and thinning of the mucous membrane of the organ.
Trichomonas
The infection multiplies rapidly and produces a substance with a similar structure to body tissues. Such a protective mechanism of Trichomonas bacteria complicates the diagnosis of the disease. Infection with vaginitis can occur after any type of sexual contact, including oral and anal, so it is impossible to provide absolute protection against infection. In very rare cases, if the rules of personal hygiene are not followed, women become infected with Trichomonas through underwear.
candida
Thrush is caused exclusively by fungi of the genus Candida, which are present in the body of every person. Yeast colpitis begins to develop when the balance of bacteria that inhibit the development of candida is disturbed. As a rule, this happens after a long treatment of a disease, after a course of antibiotic therapy. Vaginitis develops when the immune system weakens and cannot cope with the growing number of fungi in the body.
In addition, candidal colpitis appears due to a glut of the diet with carbohydrates, when taking hormonal drugs and after douching with solutions that violate the acid-base balance of the vagina. Thrush often occurs in people with diabetes or HIV, which is associated with suppressed immunity (the body does not have enough strength to fight the mycotic flora). Candidal vaginitis is often diagnosed during the last trimester of pregnancy, which is associated with a major hormonal change.

non-specific
What is non-specific vaginitis? The main stimulating factor of the disease is a violation of the microflora of the genital organs. When the number of pathogenic bacteria prevails, nonspecific colpitis begins. The disease can contribute to:
- infectious diseases that suppress a woman's immunity;
- mechanical, chemical or thermal injury to the vaginal mucosa;
- prolapse of the vaginal walls, other anatomical changes in the vulva;
- ignoring the rules of hygiene by a woman;
- taking antibiotics;
- pathologies of the endocrine system such as obesity, diabetes, insufficient ovarian function;
- atrophic processes, vascular changes in the vaginal mucosa during menopause;
- allergic reactions provoked by hygiene products, contraceptives;
- disruptions at the hormonal level.
senile
With a decrease in the amount of estrogen produced by the ovaries, age-related colpitis in women can develop. Another possible cause of the disease is the thinning of the vaginal epithelium. As a rule, vaginitis is diagnosed in elderly patients, but in rare cases it also occurs in young women. Inflammation of the vagina sometimes manifests itself in artificial menopause.
Lack of estrogen is almost always accompanied by proliferation of vaginal tissues, inhibition of the secretion of local glands, degeneration of the mucous membrane of the genital organs. This leads to the activation of the pathogenic microflora of the vagina, as well as the simplification of the penetration of harmful bacteria from the outside. As a result, the mucous membrane of the organ becomes inflamed and senile colpitis begins to develop.

Symptoms of colpitis
The symptoms of vaginitis depend on the severity, type of pathogen, and severity of the pathology. For the acute form of the disease, the following symptoms are characteristic:
- burning, itching, irritation on the external genitalia;
- pain localized at the bottom of the peritoneum;
- discharge during colpitis has an unpleasant odor and an admixture of blood (in addition, they can be purulent);
- when urinating, a woman may feel pain;
- there is redness, swelling of the mucous membrane of the genital organs (both internal and external).
In the chronic form of vaginitis, the pain is insignificant or completely absent, the woman feels normal, but her libido decreases. The course of colpitis is sluggish, however, exacerbations occur periodically, in which patients may feel itching / burning / soreness in the genital area. Sometimes a chronic disease is accompanied by urethritis, cervicitis, or pseudo-erosion of the uterine cervix.
Diagnostics
Before making a diagnosis of colpitis, the doctor collects an anamnesis and conducts a comprehensive examination of the patient, consisting of:
- examination of the cervix, vaginal walls with the help of gynecological mirrors;
- examination of the urethra, clitoris, labia, thighs for redness, swelling, cracks, ulcers;
- palpation of the uterus, appendages to identify complications of vaginitis.
In addition to the above measures, colpitis in gynecology is diagnosed with the help of mandatory laboratory tests. These include:
- microscopic examination of discharge from the cervical, urethra, posterior wall of the vagina;
- PCR analysis for the detection of genital infections;
- culture of vaginal discharge to determine the type of pathogen and the sensitivity of pathogenic bacteria to antibiotics.

Colpitis treatment
It is possible to treat the disease only after it is established to excite it. At the same time, therapy consists not only in suppressing pathogenic microbes, but also in restoring healthy microflora, strengthening immunity. How to cure colpitis? The first thing that doctors advise women is to observe sexual rest (sexual activity not only exacerbates the symptoms of pathology, but also accelerates the spread of infection throughout the body). In addition, patients with vaginitis are prescribed a special diet, which implies the rejection of salty, spicy, sweet foods and alcoholic beverages.
If, as a result of the tests, a specific causative agent of vaginitis was identified, the patient's sexual partner should also be treated. In a serious condition of the patient, with severe discomfort in the vaginal area and a significant increase in body temperature, the doctor may prescribe a course of antibiotics. A mandatory therapeutic measure for vaginitis is strict adherence to intimate hygiene (procedures are performed several times a day).
medicine
With chronic disease or its severe course, a woman is prescribed oral and intramuscular drugs. If a specific colpitis was diagnosed, the causative agent of which was gonococci, antibacterial treatment is indicated. In this case, antibiotics are administered intramuscularly for colpitis of the cephalosporin group or tetracycline drugs.
Trichomonas vaginitis is treated with nitroimidazoles such as Metronidazole, Tinidazole or Trichopolum. In a severe non-specific disease, broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy is required, for example, Amoxiclav, Azithromycin, etc. Colpitis of a fungal nature is treated with the following tablets:
- Orungal;
- Fluconazole;
- Pimafutsin, ave.
Candles
As a local therapy for vaginitis, suppositories and vaginal tablets are used. How to treat colpitis in women:
- Polygynax (has an antifungal, antibacterial effect, relieves inflammation);
- Terzhinan (has an action similar to Polygynax);
- Dalacin ointment (suppresses pathogenic flora, eliminates the inflammatory process);
- Klion-D (has an antifungal, antimicrobial effect);
- Hexicon (has an antibacterial effect, the drug is effective against most pathogens of colpitis, vaginosis and other sexual diseases).
Treatment with folk remedies
Alternative medicine methods can be used as an addition to the medical therapy of colpitis, but they cannot replace a full-fledged treatment. Douching, baths, tampons with decoctions of medicinal herbs and other means are used against vaginitis. Alternative treatment of atrophic colpitis or another type of disease includes the following methods:
- Douching with a decoction of chamomile from genital infections. 2 tbsp follows. l. brew herbs in a liter of boiling water, leave for 15 minutes, then drain and wait until the liquid has cooled. Douching is carried out daily at night until the symptoms disappear.
- Herbal bath against colpitis. The coltsfoot, St. John's wort, nettle, buckthorn bark, thyme are brewed in equal quantities, the broth is insisted for a couple of hours. After the liquid is filtered, heated to a warm state, poured into a bowl. Women should take a bath every day for 10-15 minutes.
- Tampons with infusion of calendula from vaginitis. Brew 2 tbsp. l. dry herbs in a glass of boiling water. An hour later, when the liquid is infused, it is filtered through cheesecloth, folded three times. The resulting infusion is impregnated with a hygienic tampon, after which it is placed in the vagina. It is worth doing the procedure for an infectious disease at night every day for a week.

What is dangerous colpitis
Without proper treatment, the disease causes serious complications. From the mucous membrane of the vagina, the infection gradually rises to the urethra, rectum, cervical canal, appendages. This can lead to infertility, cervical erosion, endometritis. Such complications of colpitau women often occur as a result of sexual intercourse during menstruation (this contributes to the opening of the uterine cervical canal).
Prolonged lack of treatment increases the risk of complications. A guaranteed consequence of ignoring the disease is its transition to a chronic form, when periods of improvement at the slightest weakening of immunity are replaced by exacerbations of the woman's condition. The launched inflammatory process in the vagina leads to the fusion of its walls, the development of serious inflammatory diseases of the appendages / uterus, the inability to have children or an ectopic pregnancy.
Prevention
To prevent the development of an inflammatory process in the vagina, a number of rules should be followed. Prevention of colpitis includes:
- use of condoms during casual sexual intercourse;
- refusal of underwear made of synthetic materials;
- regular observance of intimate hygiene;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle by a woman (without bad habits, with regular sports);
- the use of tampons / pads without fragrances;
- the use of intimate hygiene products with a neutral acid-base balance;
- regular strengthening of immunity, taking vitamin complexes during the off-season.