Symptoms and treatment of epididymitis in men, what is dangerous inflammation of the epididymis
The epididymis is an important part of the male reproductive system. It is he who is responsible for the selection of healthy spermatozoa and their maturation. About half of the spermatozoa die in the epididymis due to the presence of a defect and are resorbed by the epithelium. The rest, mixing with the secret, exit through the vas deferens.
The appendage is a paired organ located along the posterior edge of the testicle.
What is epididymitis?
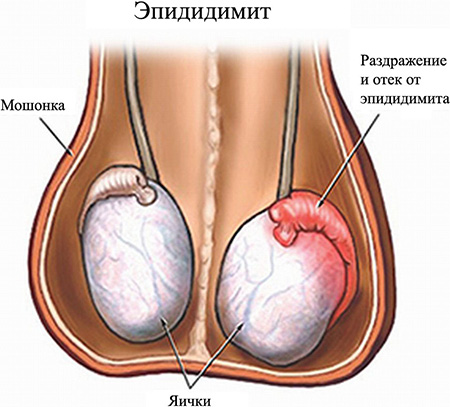
Epididymitis is an inflammation of the epididymis in men. The process is more often unilateral, but in advanced cases it also extends to the second appendage.
The inflammatory process can proceed as acute epididymitis (the most common variant of the course) or chronic (develops in the absence of adequate treatment six months after the onset of the disease).
Predisposing factors for the onset of the disease are:
- scrotal injury;
- the presence of STIs (syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia);
- inflammatory processes in other organs of the genitourinary system (urethritis, prostatitis, orchitis, cystitis);
- prostate adenoma;
- hypothermia;
- previous infectious diseases (parotitis, influenza, tonsillitis);
- conducting medical manipulations in the genitourinary system (catheterization, cystoscopy);
- sterilization operation.
Important! A separate form of epididymitis of the epididymis is the process of tuberculous etiology. More often it is secondary and is almost asymptomatic.
Symptoms of epididymitis in men
The clinical picture of an acute inflammatory process is very typical. It begins with a sharp rise in temperature to 39 ºС and above. There is weakness, dizziness, sweating.
Another important symptom of epididymitis is pain. It appears on the affected side along the posterior surface of the scrotum. It tends to radiate to the perineum, to the inguinal region, sometimes to the lumbar and sacral part of the spine.
On palpation of the appendage, it is dense, enlarged in size. Any touch is accompanied by increased pain.
Chronic inflammation proceeds with a less vivid clinical picture and is bilateral. Usually it is accompanied by periodic exacerbations, manifested by the occurrence of acute pain and a sharp increase in temperature. Between periods of exacerbation, subfebrile condition may persist, as well as weak aching pulling pains in the scrotum.
The very process of ejaculation is very painful.
Important! The most difficult to diagnose is epididymitis in boys under one year old. Most often, the clinical picture is accompanied by a sharp increase in temperature, nausea, vomiting in a child, his anxiety, screaming, crying. In the absence of objective causes of this condition, it is necessary to examine the scrotum to confirm or exclude the diagnosis of epididymitis.
Why is epididymitis dangerous?
The inflammation of the appendage itself is not a life-threatening condition and often resolves on its own after 7-10 days, however, in this case, there is a high probability that the process will become chronic.
There are complications of epididymitis that will not lead to the death of a person, but can significantly reduce the quality of his life:
- Infertility is the most frequent and irreversible complication of this disease. It develops in the chronic form. This is due to the growth of connective tissue in the cavity of the appendage, which closes the vas deferens. Obstructive obstruction occurs.
- Spread of the inflammatory process. Often, the untreated process passes to the testicular tissue, causing orchitis. This is another reason for the development of infertility, which is also obstructive in nature.
- Suppuration of the appendage. As a result, tissue melts, and pus enters the scrotal cavity, causing inflammation. If left untreated, a fistula forms between the scrotum and the environment.
Survey
Diagnosis of the disease begins with clarification:
- patient complaints (acute pain, fever);
- anamnesis of the disease (how long the disease lasts, whether there were previously similar episodes, what preceded their development);
- anamnesis of life (trauma of the scrotum, past infectious diseases).
Important! With epididymitis, this examination is very painful, so it is carried out carefully, without causing additional discomfort to the patient.
Prostate examination is an integral part of the diagnosis of epididymitis. Its digital palpation is carried out through the rectum. This will help diagnose the presence of prostate adenoma.
Of the laboratory methods used:
- complete blood count (leukocytosis, neutrophilia, increased ESR);
- general urinalysis (leukocyturia, bacteriuria, hematuria is possible with trauma);
- three-glass urine sample;
- microscopy and culture of a smear from the urethra;
- blood tests for syphilis;
- examination of scrapings of the urethral mucosa for the presence of mycoplasmas and chlamydia.
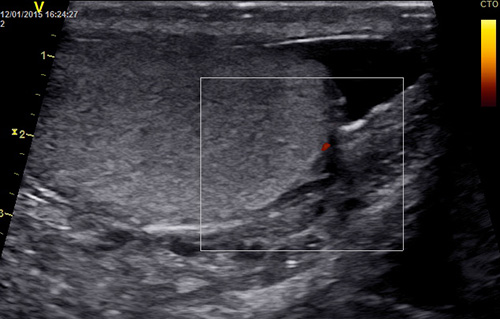
Of the instrumental methods, ultrasound of the scrotum is most often performed.
Less often, CT is used in the study of the appendage. This study is carried out for the differential diagnosis of epididymitis with a hernia, oncological diseases.
How to treat epididymitis?
Treatment of epididymitis in men should be started as early as possible. this will reduce the likelihood of infertility. Therapy is carried out most often at home, however, if purulent complications occur, the patient is hospitalized. Mode - strict bed.
The diet is aimed at eliminating any aggressive food (spicy, salty, peppery, etc.).
To reduce swelling and pain, compresses are used: a cold object or ice is wrapped in soft tissue and applied to the affected area for 15-30 minutes, then a break of 1-2 hours.
An obligatory component of the treatment of epididymitis is antibiotic therapy. It is usually prescribed empirically. Antibiotics of choice - penicillins, cephalosporins, macrolides.
Additionally, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, immunostimulating drugs, as well as vitamins can be prescribed.

In the chronic course of the process, physiotherapy procedures are added to the treatment.
Purulent epididymitis is an indication for surgical treatment (opening and drainage).
In the absence of the effect of conservative treatment, it is possible to perform an operation to remove the appendage.
Important! After completing the course of antibiotic therapy and complete recovery, it is necessary to see a urologist at least once every six months for three years.
Epididymitis can be prevented! To do this, you must comply with a few simple requirements:
- refusal of casual sexual relations;
- use of barrier methods of contraception;
- timely treatment of other inflammatory diseases of the urogenital tract (urethritis, cystitis, prostatitis);
- personal hygiene;
- exclusion of traumatic injuries of the scrotum.